Chemoreceptors/Chemical receptors
(Nose & Tongue)
NOSE
The receptors which are
sensitive to smell and taste are called as chemoreceptors.
Smell and taste are the chemical senses and the other senses
like sound and light are the physical
senses. The chemical senses always depend on the chemical nature of
substance and its solubility in water.
ü The
receptors for sense of smell - Nose
ü The
receptors for sense of taste – Tongue
So, there is a close relationship between these two
receptors, hence we are enjoying the smell and taste of the food.
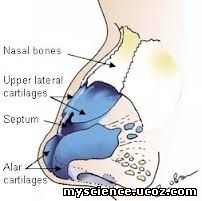
Structure of Nose
·
It is divided into small external and long
internal positions.
·
External portion is present on the face and internal portion is separated
by a bone or cartilage consisting of
two nostrils.
·
Smell is detected by these nostrils i.e... Upper nasal cavity and lower vestibular cavity.
·
Nasal cavity is lined with mucous membrane which secrets mucous to keep the membrane moist and
supplied with number of blood vessels
containing different types of chemoreceptors cells called as olfactory receptors.
·
These receptors consists cilia which projects into nasal cavity and responsible for sense of smell.
Working process of the nose to the brain
by olfactory nerve
·
When air enters the nose the chemicals which are
present in the air dissolve in moisture present on mucous membrane. These
chemicals are detected by olfactory
receptors.
·
From the base of the receptor cell, nerve fibres
from different cells pass through the holes present on a plate bony septum which separates the nasal
cavity from the rest of the skull.
·
Later these nerve fibres joins to form a large
nerve called as olfactory nerve which
detects the smell and sends the information to the brain .(analyses the sense of smell).
Relationship between nose and tongue
There is a close relationship
between smell and taste because without smelling we cannot eat. Whenever we
smell the food then only we can say the taste of the food. Sometimes we feel
the food to be tasteless if we cannot smell it.
ü
Example:
Cold, blocked nose. We can also notice that sometimes mere smell of the food
tells us the taste of the food and results in mouth watery.
TONGUE
It is the gustatory
organ which perceives the taste of the substance and gives the sense of the
taste.
In vertebrates
except in fishes taste receptors are
present on the tongue is absent hence taste receptors present at different
locations on the body.
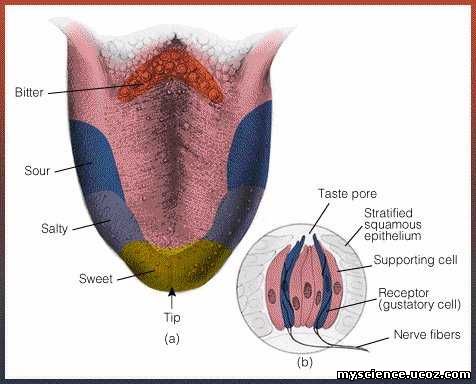
Structure of tongue
The human tongue consist about 10,000 taste buds distributed all over the tongue (dorsal and
ventral sides). Each taste bud consist two
types of cells as follows
Taste receptors
·
About 5-20
taste receptors are present in the taste
bud.
·
Each taste bud contains a small pore like
opening on the tongue called as taste
pore.
·
Each receptor cell consists free hair like cilium which projects into the cavity,
inside this saliva baths the
receptor cells
Supporting cells
·
These cells support the taste receptors
consisting about 60-20 spindle
shaped cells.
·
There are 4
types of taste receptors distributed at different locations as follows
ü Sour
taste receptors: present at along the tongue.
ü Bitter
taste receptors: present at back portion of tongue.
ü Sweet
taste receptors: present at front portion of tongue.
ü Salt
taste receptors: present at front portion of tongue.
o
Hot taste
receptors: really it is not a taste just it is a physical sensation which
irritates tongue, sour, tongue, can also sense the temperature.
Working process of
tongue to the brain by nerve fibres
·
When the food enters the mouth it gives taste to
the food and dissolve in saliva.
·
Through the taste
pore saliva enters the cavity of taste bud and baths the taste receptors.
·
The receptors come into contact with chemicals and dissolves in the saliva
generating small electrical potential.
·
Then the nerve fibre gives off and carries the
information to the brain (analysis
the sense of taste).





