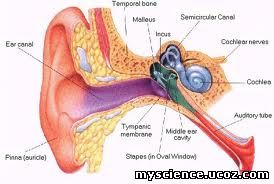
Ear
It is a small part of complex organ
situated in the skull behind the eyes. A pair of well developed ears is present
in all mammals.
Ear is the small part of the hearing organ which is present
externally and rest of the parts located inside the head/skull. The main
functions of the ear are
ü
Hearing.
ü
Maintenance of equilibrium: balancing,
controlling.
Ø Structure
The
ear is divided into three regions. They are:
ü External
ear
ü Middle
ear
ü Internal
ear
·
External
ear or Ear pinna
o It
is the visible part of the ear made up of cartilage
covered by the skin.
o Movable
pinna is present composing of fibre,
elastic cartilage which is
deeply grooved and ridged to receive the sound vibrations from all the
directions.
o A
narrow a tube is present known as auditory
meatus connects to the ear (present between pinna and ear drum).
o At
the end of the narrow tube a delicate membrane is present known as ear drum / tympanum/ tympanic membrane.
o It
is a narrow tube containing hairs
and glands (ceruminous secretes
cerumin) helps to removes the dust particles entering into the ear.
§
Ear drum:
it is oval in shape which separates the external ear from the middle ear, it is
delicate and essential to hear.
·
Middle
ear
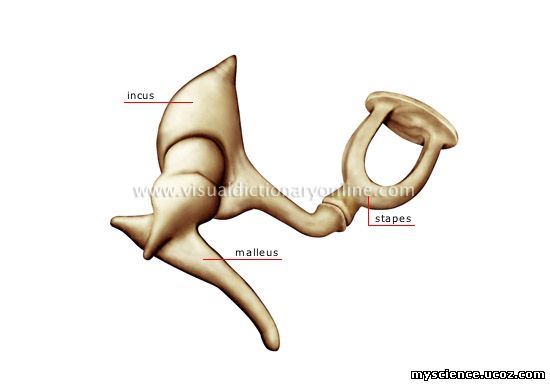
It is irregular in shape which is made up of three tiny bones known as ossicles as follows
o Malleus/hammer: It is attached to the
ear drum and look like a hammer shape consisting of head, neck and handle.
o Incus/Anvil: It is the middle bone
looks like an anvil shape present in the cavity of malleus.
o Stapes/Stirrup – It is connected to the
internal ear looks like a stirrup shape consisting of head, neck, two limbs and
base.
Working process of Middle ear
·
It is separated from the internal ear by a bony
septum known as fenestra rotundus or
round membrane.
·
The stapes
fix into one more membrane known as fenestra ovalis or oval membrane.
·
This is connected to the cavities of the mouth
by a narrow tube called as eustachain
canal which helps in maintaining equal pressure on both sides of the tympanum.
·
Internal
ear It is the actual part of the ear which
involves in hearing consisting two
cavities as follows: o Outer bony labyrinth: It is the outer
cavity located in the bone of skull filled with the fluid Perilymph.
o Inner membranous labyrinth: It is the
inner cavity surrounded by membrane filled with a fluid Endolymph.
·
Membranous
labyrinth: It is divided into three parts namely
ü Vestibule
ü Semi
circular canals
ü Cochlea
In this, vestibule
and semi circular canals maintain
the balance of the ear and cochlea
is for hearing.
·
Semicircular
canals and Vestibule
o They
have no auditory functions but useful for balancing.
o The
base of these canals contains swellings known as ampulla which opens into utricle
and connects to sacculus.
o The
sacculus gives rise to coiled structure known as cochlea.
·
Structure
of Cochlea
o It
is the spiral, coiled structure divided into three chambers as scala vestibule, scale media and scala tympanum.
o Scala
media is filled with a fluid known as Endolymph
and has a special sensory cells forming organ of corti which is useful for hearing.
Ø Working process of the ear to the brain
by auditory nerve
·
The sound waves which are coming from the
environment enter to the tympanic
membrane to the external ear.
·
These waves transmit to the endolymph by the ossicles.
·
These ossicles create the vibrations in the endolymph
of the inner ear.
·
Then these vibrations receive by the cochlea through organ of corti to the brain with the help of auditory nerve.
| 




