|
ROOT SYSTEM
It is the underground main axis of the plant body which is brown in
colour developing from the embryo. Root system is of two types as follows:
Ø
Tap Root System (Found in Dicot
plants)
·
The
main root develops from the radicle (first part of the seed) of the germinating
seed known as primary roots or tap root.
·
Later
the taproot develops into lateral roots known as secondary roots bearing rootlets and root hairs known as tertiary roots(helps to absorb the
water from the soil)
Examples: Maize, Carrot, Raddish, Mango etc.
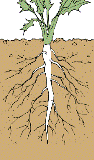 
Tap roots Fibrous roots
Ø
Fibrous Root System (Found in Monocot
plants)
·
The
radicle of this is short lived and degenerates many new roots developing from
the base of the stem in the form of fibres,
hence known as fibrous root.
·
If
the root develops from the other parts of the plant except from the radicle
known as adventitious roots.
Examples; Bean, Paddy, Marigold etc.
Ø
Zones/Regions of a Typical Root
·
Root Cap Zone
§ It is cup shaped structure covered
with the tip of the root.
§ The root apices are covered with root
cap from from the meristematic tissue known as calyptrogen.
§ The root cap is replaced by root
pockets in hydrophytes. Example:
Pistia, Lemna.
§ It gives protection to the root cap.
·
Root Hair Zone
§ It is present above elongation zone.
§ It produces cluster of fine thread
like structures known as root hairs.
§ Root hairs arise from the epidermal
cell hence it is known as piliferous
layer.
·
Elongation Zone
§ It is present above the meristamatic zone and behind the root
cap.
§ In this zone newly formed cells
expands and elongates linearly to increase the length of the root.
·
Maturation Zone
§ It is present above the root hair
zone.
§ The tissue in this zone develops into permanent tissue.
§ In this zone secondary growth takes
place along with the conduction of water and mineral salts.
Ø
Characters
·
Root
is differentiated into nodes and internodes.
·
Leaves
and normal buds are absent.
·
Root
apex is protected by root cap.
·
Root
hairs are unicellular in nature.
·
Root
grows underground in -vely geotropic (or) –vely phototropic manner.
Ø
Functions
·
It
helps in fixing the plants in the soil.
·
It
helps in absorption of water and mineral salts from the soil.
·
It
helps in conduction of water to the stem.
·
It
stores the food materials to perform different functions.
<<<<<<<<<<<<THE END>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
| 




