Parasites
The
association between two animals in which one animal gets food and shelter
(parasite) from the other animal (host) are known as Parasites.
Based
on the location on (or) in the body host parasites are of two types
·
Ectoparasites:
The parasite which lives on the external surface of the body of host. They
consists claws for clinging to the external surface of host and with anti-coagulant substances in their saliva.
Examples:
lice, mites, ticks, etc., mosquitoes, leeches.
 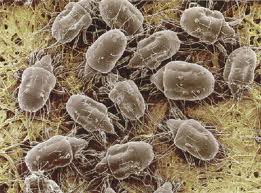
Ticks Mite
·
Endoparasites:
The parasite which lives inside the body of host.
A thick
cuticle is present instead of epidermis in endoparasites which gives protection
to the parasite against the action of digestive
juices of host.
They show
well developed organs like hooks and suckers for attachment to the host and
get the predigested food hence digestive system is reduced/ absent but with well developed reproductive system. These
parasites have the capacity to secrete ‘antienzymes’ (neutralizes digestive
enzymes of host).
Examples: Tapeworm, Filarial worm.
Tapeworm
·
Commonly known as Pork worm.
·
Scientifically known as Taenia solium.
·
Belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes.
·
Lives in the intestine.
·
Mode of disease transmission is contamination.
·
Leads to
disease known as Taeniasis.
·
Completes life cycle in two hosts i.e., man and pig.
·
Symptoms:
loss of weight, appetite, indigestion, nervous disorders.
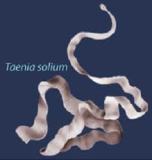 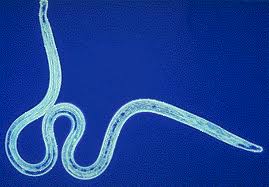
Tapeworm Filarial
worm
Filarial worm
·
Scientifically known as Wuchereria bancroftii.
·
Belongs to the phylum Nematahelminthes.
·
Adult: Lives in the lymph glands/lymph vessels.
·
Larvae: Lives in the blood.
·
Mode of disease transmission is contamination.
·
Leads to disease filariasis or elephantiasis.
·
Complete life cycle in two hosts i.e., man and female culex mosquito.
·
Symptoms:
o
Swelling of lymph gland/vessels (particularly in
scrotum of man and arms, legs)
o
Skin becomes thick, hard and dry with disappearance
of sweat glands, fever.
Parasitic Adaptations
The parasites show some changes and modifications to lead
the life in the host known as Parasite adaptations.
Based on their location inside the body they are of 3 types.
1.
Coelozoic
parasites
The parasites
which lives inside the body cavity of host.
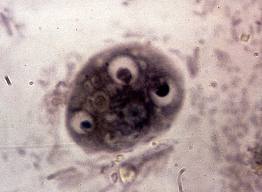
Entamoeba histolytica
·
Belongs to the phylum Sarcomastigophora.
·
Lives in the large intestine.
·
Mode of disease transmission is contamination.
·
Important feature of parasite is the presence of
RBC in the food vacuole.
·
Leads to a disease Amoebiasis/Amoebia dysentery.
·
Completes its life cycle in one host i.e., man
·
Symptoms:
abdominal pain, frequent motions (blood and mucosa) Indigestion
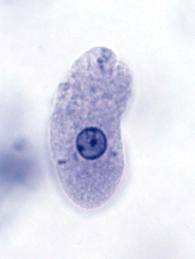  
E.hystolitica P.vivax T.gambiense
Intracellular/Cytozoic
parasites:
The parasites which lives inside
the cells of the host tissues.
Malarial parasite
·
Scientifically known as plasmodium vivax.
·
Belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa.
·
Lives in the RBC’s and liver cells in
man.
·
Leads to a disease malaria.
·
Mode of disease transmission is contamination.
·
Infective stages are sporozoites in man
·
Completes its life cycle in two hosts i.e., man and female anopheles mosquito.
·
Symptoms
o
Cold
stage: Severe chill, shivering, head ache
o
Hot stage:
high fever (rises up to 107F), rise of pulse.
·
Species which causes malaria are
o
P.vivax:
Benign tertian fever
o
P.ovale:
Mild tertian fever
o
P.malariae:
Quartan malaria fever
o
P.falcipurum:
Malignant tertian/Black water fever.
Inter/extra/Histozoic
parasites
The parasites which lives in
between the cells of the host tissues/organs.
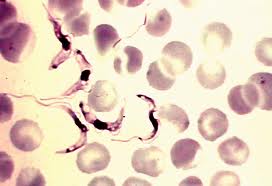
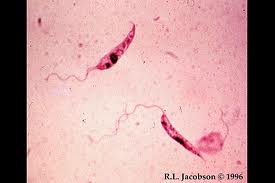
Trypanosoma gambiense
·
Commonly known as African Sleeping Sickness.
·
Belongs to the phylum Sarcomastigophora
·
Lives in the blood and Cerebro Spinal fluid (CSF) of man
·
Leads to a disease transmission is contamination.
·
Infective stages is metacyclic
·
Completes its life cycle in two hosts i.e., man and tse tse fly
·
Symptoms
o
Regular fever head ache,Muscular
weakness, unconscious.
Some Other Parasites Entamoeba
gingivalis
·
Belongs to phylum Sarcomastigophora.
·
Lives in the mouth of man.
·
Leads to a disease periodontal.
·
Mode of disease transmission is contamination.
·
Completes its life cycle in man.
·
Symptoms:
bleeding in the gums.
Leishmania
donovani
·
Belongs to the phylum Sarcomastigophora.
·
Lives in the tissue, spleen and bone
marrow.
·
Mode of disease transmission is contamination.
·
Leads to disease kala-azar.
·
Symptoms:
fever, enlargement of liver and spleen.
·
Completes its life cycle in man
Giardia
intestinalis
·
Commonly known as Grand old man of intestine.
·
Belongs to the phylum Sarcomastigophora.
·
Lives in the small intestine of man.
·
Leads to a disease diarrhoea.
·
Mode of disease transmission is contamination.
·
Symptoms:
frequent motions.
·
Completes its life cycle in man.
    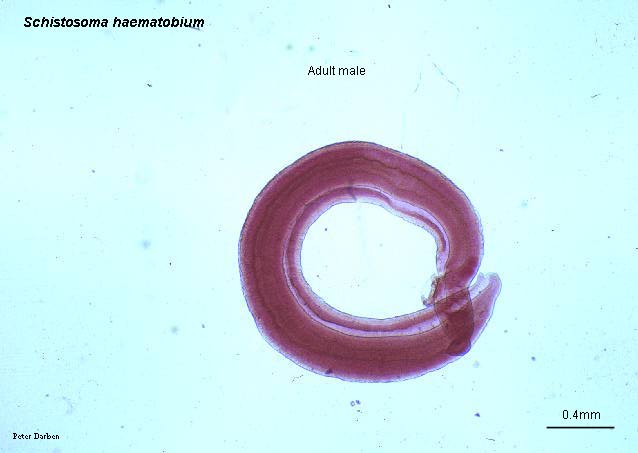
E.gingivalis
L.donovani G.intestinalis A.lumbricoides S.haemotobium
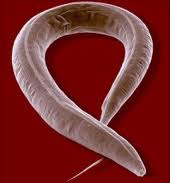
Ascaries
lumbricoides
·
Commonly known as round worm.
·
Belongs to the phylum Nematahelminthes.
·
Lives in the intestine of man
·
Leads to a disease ascariasis.
·
Mode of disease transmission is contamination.
·
Symptoms:
Stunted growth (children)
Indigestion,
loss of weight, pneumonia
·
Completes its life cycle in man.
Schistosoma
haemotobium
·
Commonly known as blood fluke.
·
Belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes.
·
Lives in the pelvic veins of man
·
Leads to a disease schistosomiasis.
·
Mode of diseases transmission is contamination.
·
Completes its life cycle in man.
·
Symptoms
o
Haematuria (release of blood through urine)
o
Swimmer’s itch(larva penetrates causing
irritation)
| 




