Brown Rust of Wheat
Host: Triticum
aestivum Systematic Position
Pathogen: P.recondita Division:Basidomycota
Sub-division:Basidomycotina
Class:Pucciniomycetes
Order:Pucciniales
Family:Puccinniaceae
Genus:Puccinia
Species:recondita
Introduction
This
is the common blast disease in India. Mainly the damage is done is due to the
leaf rust causing loss at about 25% in the yield and also due to destruction of foliage, sterility of spikelet’s and
production of shriveled grains.
The
pathogen affects the plants in three
types of rusts namely:
·
Stem/black
rust: P.graminis
·
Stripe/yellow
rust: P.striformis
·
Leaf/brown
rust: P.recondita
Symptoms
·
Small
brown pustules develop on the leaf
blades in an irregular manner.
·
Orange
colour pustules are formed on the
upper surface of leaves.
·
Rupturing of leaf takes place in the pustules
region.
·
Pustules
are also formed on leaf sheaths and stalks.
Casual organism
The fungus "Puccinia recondita” causes leaf rust disease of wheat.
Structure of fungus
They are three types of spores namely:
·
Urediospore: reddish spore is present on the rust
leaf, single celled, brown and spherical
·
Teleutospore: club shaped spore is present on the
rust leaf , two celled, brown, flat-conical
·
Basidiospore: resting spore of the rust leaf
(produced in late summer) single celled, pale with oval-oblong.
Disease Cycle
Urediospore
is the primary spore form involved
in infecting the wheat crop. These spores are carried by wind and germinate by
falls on moist leaf leading to "secondary
infection”.
 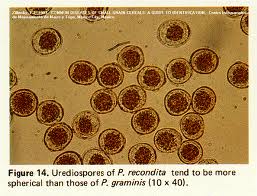  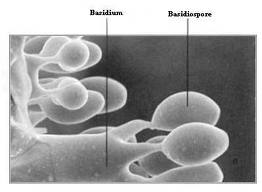
Infected leaf Urediospore Teleutospore Basidiospore
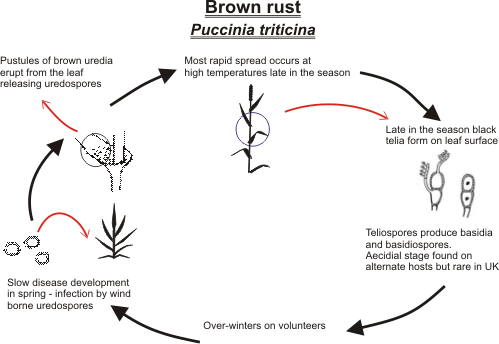
Disease Cycle
Favorable conditions
·
High
humidity i.e., 90%
·
Optimum
temp., i.e., 15-20⁰c
Control measures:
·
Using
disease resistant varieties
·
Changing
the crop frequently
·
Field
sanitation
·
Use
of fertilizers: N.P.K(same ratio)
·
Use
of fungicides like Sulphur, Dithane, Zineb,
Bayleton
| 




