Ø Gynoecium It is the essential organ consisting style, ovary also known as megasporophyll.
They participate in sexual reproduction which produces seeds and fruits, also
known as carpels or pistil.
·
Structure of Pistil
ü Ovary : Basal
swollwn part.
ü Style:
Elongated part of the ovary.
ü Stigma: Tip of
the style.
·
Types of Ovary
Based on the position of the ovary they are of three
types as follows
o Superior / Epigynous flower
The floral parts are arranged below the ovary on the
thalamus. Example: Hibiscus.
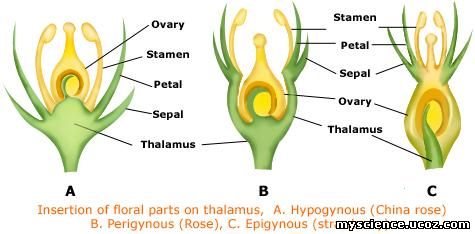
o Half superior/Half inferior/ Perigynous flower
The floral parts are arranged at the same height of the
ovary on the thalamus. Example: Dolichos.
o Inferior/Hypogynous flower
The floral parts are arranged above the ovary on the
thalamus. Example: Tridax
Based on the number of carpels they
are of many types as follows
ü
Monocarpellary: Ovary with one carpel. Example: Dolichos
ü
Bicarpellary: Ovary with two carpels. Example: Brassica
ü
Tricarpellary: Ovary with three carpels .Example: Ricinus
ü
Tetracarpellary: Ovary with four carpels.Example: Oenothera
ü
Pentacarpellary: Ovary with five carpels.Example: Hibiscus
ü Multicarpellary:
Ovary with many carpels.Example: : Annona
Based on the fusion of the carpels
they are of three types as follows
·
Apocarpous: Carpels present on the thalamus
remains free. Example: Lotus.
·
Sub apocarpous: Carpels present on the thalamus are
partly fused and partly free. Example: Lotus.   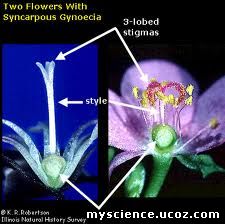
·
Syncarpous: Carpels present on the thalamus are
fused. Example: Calotropis
Ø Locules in Ovary
The cavities present in the carpels are known as locules which are different from species
to species as follows
·
Unilocular: Carpels with one locule. Example:
Dolichos
·
Bilocular: Carpels with two locules. Example:
Solanum
·
Trilocular: Carpels with three locules. Example:
Onion
·
Tetralocular: Carpels with four locules. Example:
Ipomoea
·
Pentalocular: Carpels with five locules. Example:
Hibiscus
·
Multilocular: Carpels with many locules. Example: Abutilon
Ø Placentation
The ovary consists of one
or more ovules and ovule is considered as megasporangium.After
fertilization ovules develop into seeds .The part of the ovary that bears the
ovules is known as placenta and the
mode of arrangement of ovules in the ovary known as placentation. They are of 7 types
·
Marginal placentation: Ovary is monocarpellary and
unilocular. Example: Dolichos
·Parietal placentation: Ovary is bicarpellary and
unilocular. Example: Brassica
·
Axile placentation: Ovary is bicarpellary or
multicarpellary and unilocular. Example: Solanum
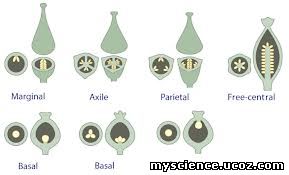
·
Free central placentation: Ovary is multicarpellary and
unilocular. Example: Dianthus
·
Basal placentation: Ovary is monocarpellary and
unilocular. Example: Tridax
·
Apical placentation: Ovary is monocarpellary and
unilocular. Example: Lotus
·
Superficial placentation: Ovary is multicarpellary, multilocular
and unilocular. Example: Lily
Ø Style
It is a adequate, stalk
like structure develops from ovary. During fertilization it acts as a guide to the pollen tube and helps to
reach ovary. Based on the position
they are of three types as follows
·
Terminal style: Develops from the apical part of the
ovary Example: Hibiscus
·
Lateral style: Develop from the side of the ovary. Example:
Mango
·
Gynobasic style: Develops directly from the base of
the ovary. Example: Ocimum
Ø Stigma
It is the terminal part of
the style which receives the pollen grains. Based on their shape and structure
they are of many types
·
Capitate : Round stigma. Example: Hibiscus
·
Plumose: Feather stigma Example: Oryza
·
Bifid : Fork stigma. Example: Tridax
·
Dumb-bell : Dumb-bell stigma. Example: Catharanthus.
·
Discoid:Disc stigma. Example: Berry.
·
Funnel : Funnel stigma. Example: Crocus
·
Linear: Lond & narrow stigma. Example: Acacia
·
Radiate: Hooked stigma. Example: Papaver
.......................THE END...........................
| 




